Argo CD Deploying an Application
Argo CD's primary job is to make sure that your desired state, stored in Git, matches your running state on your Kubernetes installation. It does this by comparing Kubernetes declarations (stored in YAML or JSON in Git) with the running state. Argo CD does this by treating a group of related manifests as an atomic unit. This atomic unit is called an Application, in Argo CD. An Argo CD Application is controlled by the Argo CD Application Controller via a Custom Resource.
You can read more about Argo CD concepts by reading the offical documentation.
Application Repo
We will be working with this example repo throughout, but for this example, we will be working within the 00-deploying-application directory. In this directory you will find:
- A Namespace
- A Deployment
- A Service
We will be deploying these as a single unit with Argo CD using the Application CR (custom resource). We can do this via the Argo CD UI. First click on the + NEW APP button on the Argo CD UI. And fill out the following.
Application Name: testProject Name: defaultSYNC POLICY: ManualRETRYEnable this, and leave the defaultsRepository URL: https://github.com/christianh814/kbe-appsRevision: mainPath: 00-deploying-applicationCluster URL: https://kubernetes.default.svcNamespace: test
NOTE: You're probably thinking "What is https://kubernetes.default.svc?" That is Argo CD's way of identifying which cluster to apply the manifests to. In this case, it's the cluster Argo CD is running on. The address https://kubernetes.default.svc is the internal Kubernetes API endpoint.
Leave everything else as the default values and click CREATE.
You should see your Application as "Missing" and "OutOfSync"
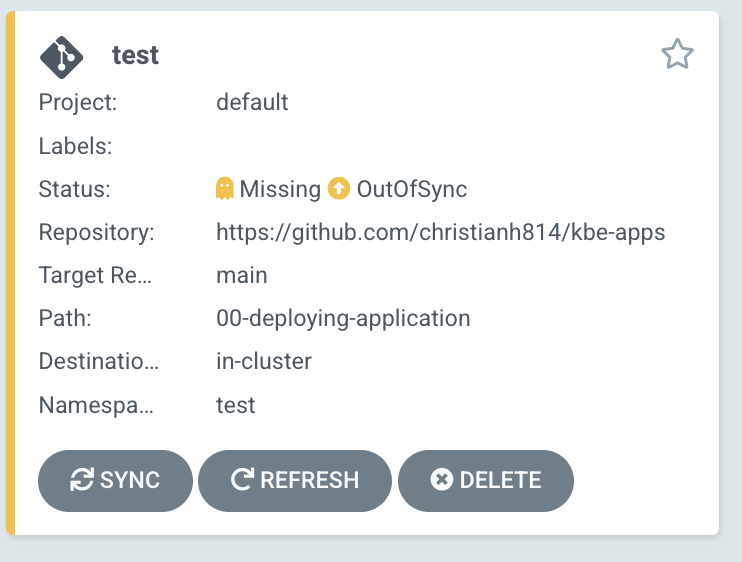
Verify that your Application is not on your cluster by running kubectl get all -n test
$ kubectl get pods -n test
No resources found in test namespace.
You can also see the status with the argocd cli. Run argocd app get test
$ argocd app get test
Name: test
Project: default
Server: https://kubernetes.default.svc
Namespace: test
URL: https://localhost:8080/applications/test
Repo: https://github.com/christianh814/kbe-apps
Target: main
Path: 00-deploying-application
SyncWindow: Sync Allowed
Sync Policy: <none>
Sync Status: OutOfSync from main (a9ee236)
Health Status: Missing
GROUP KIND NAMESPACE NAME STATUS HEALTH HOOK MESSAGE
Namespace test OutOfSync Missing
Service test bgd OutOfSync Missing
apps Deployment test bgd OutOfSync Missing
Click on SYNC in the Argo CD UI, then SYNCHRONIZE to apply these manifests to your cluster. After a bit, you should see your Application as "Healthy" and "Synced".

Your Application should now be running! Running kubectl get all -n test should now show your manifests applied to the cluster.
$ kubectl get all -n test
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
pod/bgd-74dc875f9b-xzzrf 1/1 Running 0 118s
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
service/bgd ClusterIP 10.96.73.254 <none> 8080/TCP 118s
NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE
deployment.apps/bgd 1/1 1 1 118s
NAME DESIRED CURRENT READY AGE
replicaset.apps/bgd-74dc875f9b 1 1 1 118s
Divergence
Argo CD has the ability to visualize any divergence in your cluster, as well as the ability to reconcile that divergence. Let's introduce a change to the cluster. Change the scale of the Deployment from 1 to 3.
kubectl scale deployment/bgd --replicas=3 -n test
This should cause the Application to have the status of "OutOfSync".
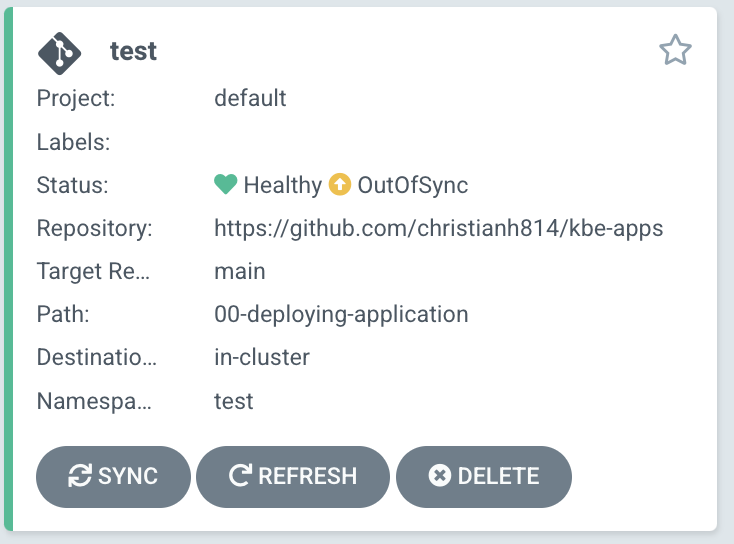
This time, we can sync the Application with the argocd cli.
NOTE: You could have also clicked "SYNC" in the Argo CD UI
argocd app sync test
Self Heal
You can setup Argo CD to automatically correct drift by setting the Application manifest to do so. You can run kubectl edit application test -n argocd and set the following configuration:
Example:
spec:
syncPolicy:
automated:
prune: true
selfHeal: true
Conversely, you can run the following command:
kubectl patch application/test -n argocd --type=merge -p='{"spec":{"syncPolicy":{"automated":{"prune":true,"selfHeal":true}}}}'
Now try introducing a change by running the same scale command: kubectl scale deployment/bgd --replicas=3 -n test
What happened? Did you change apply?
Now that you have autoheal turned on, Argo CD will keep your cluster in sync with your desired state that's, in our case, currently store in GitHub!