Guided Exercise: Connecting kubectl to Your Cluster
In this exercise you will install the kubectl command-line tool on your computer, and connect to the Kubernetes cluster that you will be using throughout the course.
Outcomes
You should be able to:
-
Install kubectl
-
Connect to Minikube (if you are using Minikube)
-
Connect to the OpenShift Developer Sandbox (if you are using the OpenShift Developer Sandbox)
Prerequisites
Ensure you have either installed Minikube or created an OpenShift Developer Sandbox account.
Instructions
The installation procedure of kubectl depends on your operating system.
1) Installing kubectl in Linux-based systems.
The Linux distributions supported in this course are Fedora Linux 34 and Red Hat Enterprise Linux 8.
You can install kubectl by downloading the binary and moving it to your PATH. At the same time, it is possible to use a package-manager.
1.1) Using curl and the binary file
-
Open a command-line terminal to download the kubectl binary.
[user@host ~]$ curl -LO https://dl.k8s.io/release/v1.21.0/bin/linux/amd64/kubectl
-
Copy the binary to your
PATHand make sure it has executable permissions.
[user@host ~]$ sudo install -m 0755 kubectl /usr/local/bin/kubectl
-
Verify that kubectl has been installed successfully.
[user@host ~]$ kubectl version --client
Client Version: version.Info{Major:"1", Minor:"21", GitVersion:"v1.21.0", GitCommit:"cb303e613a121a29364f75cc67d3d580833a7479", GitTreeState:"clean", BuildDate:"2021-04-08T16:31:21Z", GoVersion:"go1.16.1", Compiler:"gc", Platform:"linux/amd64"}
1.1) Using the dnf package manager.
-
Open a command-line terminal. Install the package by using
dnf.
[user@host ~]$ dnf install kubectl ...output omitted... ================================================================================ Package Architecture Version Repository Size ================================================================================ Installing: kubectl x86_64 1.21.1-0 kubernetes 9.8 M Transaction Summary ================================================================================ Install 1 Package ...output omitted...
-
Verify that kubectl has been installed successfully.
[user@host ~]$ kubectl version --client
Client Version: version.Info{Major:"1", Minor:"21", GitVersion:"v1.21.0", GitCommit:"cb303e613a121a29364f75cc67d3d580833a7479", GitTreeState:"clean", BuildDate:"2021-04-08T16:31:21Z", GoVersion:"go1.16.1", Compiler:"gc", Platform:"linux/amd64"}
2) Installing kubectl in macOS.
2.1) Using curl and the binary file
-
Open a command-line terminal. Download the kubectl binary by using
curl. Replace theos-architectureparameter depending on your Mac processor. If your Mac comes with an Intel processor, useamd64. If your Mac comes with an Apple Sillicon processor, usearm64.
[user@host ~]$ curl -LO "https://dl.k8s.io/release/v1.21.0/bin/darwin/os-architecture/kubectl"
-
Give the binary file executable permissions. Move the binary file executable to your
PATH.
[user@host ~]$ chmod +x ./kubectl [user@host ~]$ sudo mv ./kubectl /usr/local/bin/kubectl
-
Verify that kubectl has been installed successfully.
[user@host ~]$ kubectl version --client
Client Version: version.Info{Major:"1", Minor:"21", GitVersion:"v1.21.0", GitCommit:"cb303e613a121a29364f75cc67d3d580833a7479", GitTreeState:"clean", BuildDate:"2021-04-08T16:31:21Z", GoVersion:"go1.16.1", Compiler:"gc", Platform:"linux/amd64"}
2.2) Using the homebrew package manager
|
Note |
If you have previously installed Minikube with |
-
Install kubectl by using
brew
[user@host ~]$ brew install kubectl ...output omitted...
-
Verify that kubectl has been installed successfully.
[user@host ~]$ kubectl version --client
Client Version: version.Info{Major:"1", Minor:"21", GitVersion:"v1.21.0", GitCommit:"cb303e613a121a29364f75cc67d3d580833a7479", GitTreeState:"clean", BuildDate:"2021-04-08T16:31:21Z", GoVersion:"go1.16.1", Compiler:"gc", Platform:"linux/amd64"}
3) Installing kubectl in Windows
3.1) Using the binary
-
Create a new folder, such as
C:\kube, to use as the destination directory of the kubectl binary download. -
Download the latest release of the kubectl binary from https://dl.k8s.io/release/v1.21.0/bin/windows/amd64/kubectl.exe and save it to the previously created folder.
-
Add the binary to your
PATH.-
In the search box on the taskbar, type
env, and selectEdit the system environment variablesfrom the search results. -
Click
Environment Variableson theSystem Propertiesscreen. -
Under the
System variablessection, select the row containingPathand clickEdit. This will open theEdit environment variablescreen. -
Click
Newand type the full path of the folder containing thekubectl.exe(for example,C:\kube). -
Click
OKto save the change and close the editor. -
Click
OK→OKto close out of the remaining screens.
-
-
Verify that kubectl has been installed successfully.
[user@host ~]$ kubectl version --client
Client Version: version.Info{Major:"1", Minor:"21", GitVersion:"v1.21.0", GitCommit:"cb303e613a121a29364f75cc67d3d580833a7479", GitTreeState:"clean", BuildDate:"2021-04-08T16:31:21Z", GoVersion:"go1.16.1", Compiler:"gc", Platform:"linux/amd64"}
4) Download the DO100-apps repository
The D100-apps GitHub repository contains files used throughout the course. The best way to work with it is by using Git. However, if you are not used to Git, you can simply download it as a regular folder and place it anywhere in your computer.
4.1) Using Git
If you have Git installed in your system, you can simply clone the repository.
[user@host ~]$ git clone https://github.com/RedHatTraining/DO100-apps.git ...output omitted...
4.1) Downloading it from the GitHub web page
-
Open a web browser and navigate to
https://github.com/RedHatTraining/DO100-apps. -
Click
Codeand then clickDownload ZIP. A ZIP file with the repository content is downloaded.
5) Connecting kubectl to the Kubernetes cluster
The DO100-apps contains a script that handles all configurations for you under the setup directory. The script you should run depends on your operating system (Linux, macOS or Windows) and the Kubernetes distribution you use (Minikube or the OpenShift Developer Sandbox).
If you run the Minikube script, it will configure Minikube to work as a Kubernetes cluster with restricted access. You will only have access to two namespaces. This way, we simulate a real Kubernetes cluster, where usually developers do not have full access.
|
Note |
If you want to recover full access over your cluster, then you can change the kubectl context to the default Minikube context, |
If you run the OpenShift Developer Sandbox script, it will configure kubectl to run commands against the Openshift Developer Sandbox cluster. The script will ask you to provide some information such as cluster url, username or token.
5.1) Using Minikube
-
Linux and macOS
In your command-line terminal, move to the DO100-apps directory and run the script located at ./setup/operating-system/setup.sh. Replace operating-system for linux if you are using Linux. Use macos if you are using macOS. Make sure the script has executable permissions.
[user@host DO100-apps]$ chmod +x ./setup/operating-system/setup.sh [user@host DO100-apps]$ ./setup/operating-system/setup.sh Creating namespace 'user-dev' ... Creating namespace 'user-stage' ... Creating certificates ... Creating Kubectl credentials for 'user' ... Creating Kubectl context 'user-context' for user 'user' ... Creating role resources for user 'user' in namespace 'user-dev' ... Creating role resources for user 'user' in namespace 'user-stage' ... Switched to context "user-context". Switching to namespace 'user-dev' ... OK!
-
Windows
In your command-line terminal, move to the DO100-apps directory. Run the command Set-ExecutionPolicy -Scope Process -ExecutionPolicy Bypass. This command allows you to run unsigned PowerShell scripts in your current terminal session.
[user@host DO100-apps]$ Set-ExecutionPolicy -Scope Process -ExecutionPolicy Bypass
Run the script located at .\setup\windows\setup.ps1.
[user@host DO100-apps]$ .\setup\windows\setup.ps1 Creating namespace 'user-dev' ... Creating namespace 'user-stage' ... Creating certificates ... Creating Kubectl credentials for 'user' ... Creating Kubectl context 'user-context' for user 'user' ... Creating role resources for user 'user' in namespace 'user-dev' ... Creating role resources for user 'user' in namespace 'user-stage' ... Switched to context "user-context". Switching to namespace 'user-dev' ... OK!
5.1) Using the OpenShift Developer Sandbox
The setup-sandbox script will ask you to provide a server, a token and your username. To find the server and token follow these steps:
-
Open a web browser and navigate to the OpenShift Developer Sandbox website. Log in with your username and password.
-
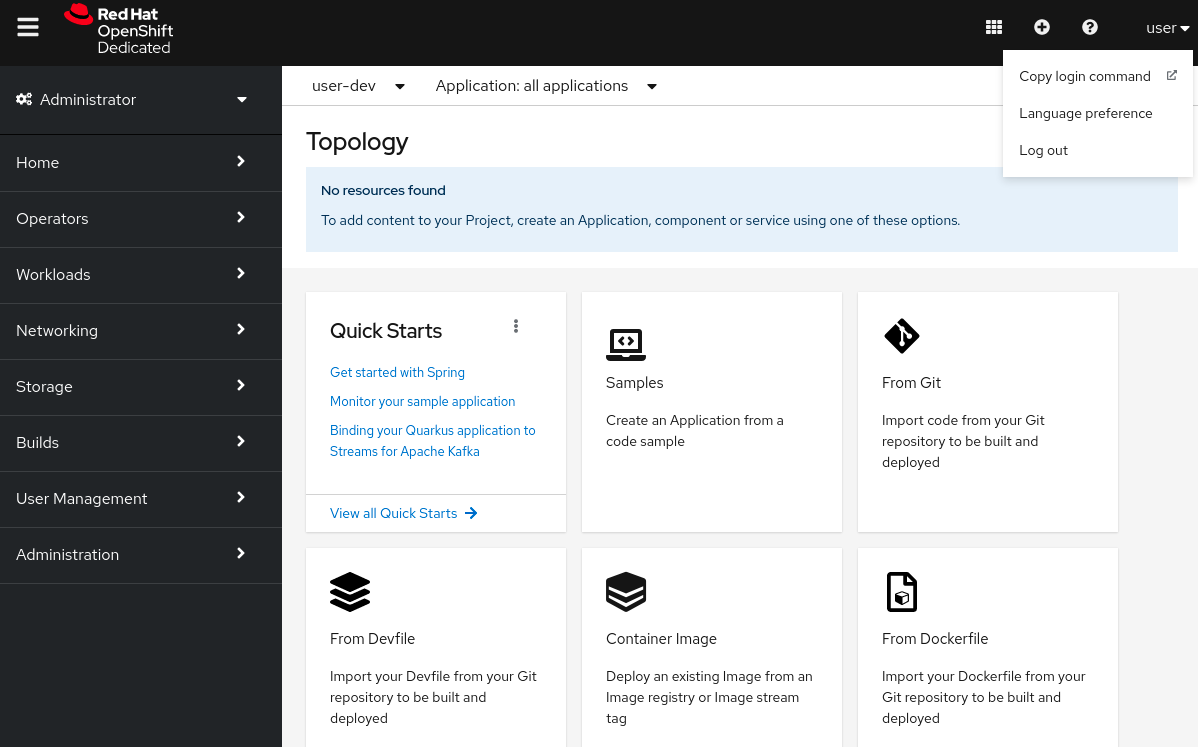
Click on your username in the upper right pane of the screen. A dropdown menu opens.
-
In the dropdown menu, click
Copy login command. A new tab opens, log in again with your account if necessary by clickingDevSandbox.
-
Click
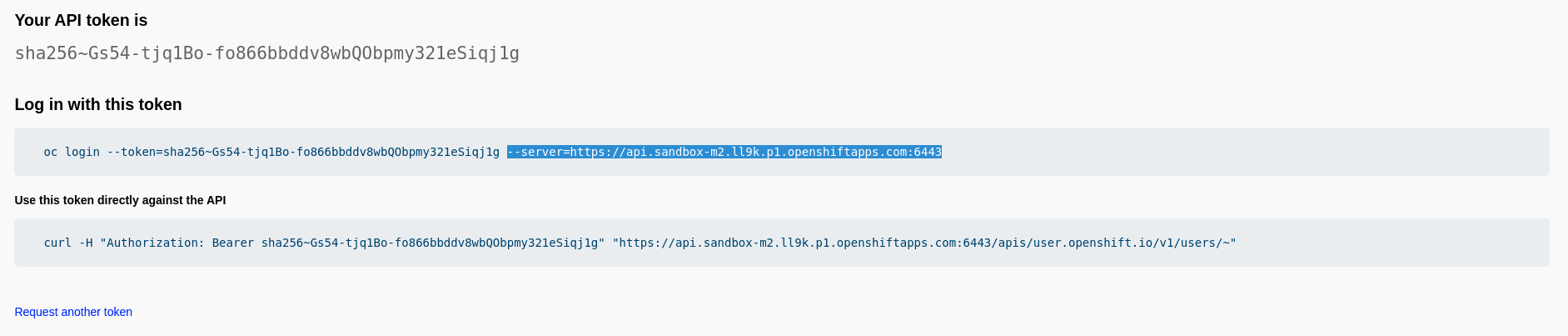
Display Token. -
The token you must provide in the script shows in your web browser.
-
The server you must provide is a parameter of the
oc login commanddisplayed. For example, in the commandoc login --token=sha256~Gs54-tjq1Bo-fo866bbddv8wbQObpmy321eSiqj1g --server=https://api.sandbox.x8i5.p1.openshiftapps.com:6443, the server is https://api.sandbox.x8i5.p1.openshiftapps.com:6443.
-
Keep these values. You will be asked for them in the script.
Run the appropiate script. The following instructions will depend on your operating system.
-
Linux and macOS
In your command-line terminal, move to the DO100-apps directory and run the script located at ./setup/operating-system/setup-sandbox.sh. Replace operating-system for linux if you are using Linux. Use macos if you are using macOS. Make sure the script has executable permissions.
[user@host DO100-apps]$ chmod +x ./setup/operating-system/setup-sandbox.sh [user@host DO100-apps]$ ./setup/operating-system/setup-sandbox.sh What is the OpenShift cluster URL? https://api.sandbox.x8i5.p1.openshiftapps.com:6443 What is the OpenShift token? sha256~wVSG...DDn0 What is your OpenShift username? user Creating Kubectl context... Context created successfully
-
Windows
In your command-line terminal, move to the DO100-apps directory. Run the command Set-ExecutionPolicy -Scope Process -ExecutionPolicy Bypass. This command allows you to run unsigned PowerShell scripts in your current terminal session.
[user@host DO100-apps]$ Set-ExecutionPolicy -Scope Process -ExecutionPolicy Bypass
Run the script located at .\setup\windows\setup-sandbox.ps1.
[user@host DO100-apps]$ .\setup\windows\setup-sandbox.ps1 What is the OpenShift cluster URL? https://api.sandbox.x8i5.p1.openshiftapps.com:6443 What is the OpenShift token? sha256~wVSG...DDn0 What is your OpenShift username? user Creating Kubectl context... Context created successfully
This concludes the guided exercise.